AWS vs. Azure – A brief guide on main differences
October 21, 2022
Enterprise spending on cloud infrastructure has grown tremendously in recent years, surpassing the $50 billion mark in Q4 last year. Gartner predicts worldwide end-user spending on public cloud is expected to reach nearly USD 600 billion in 2023.
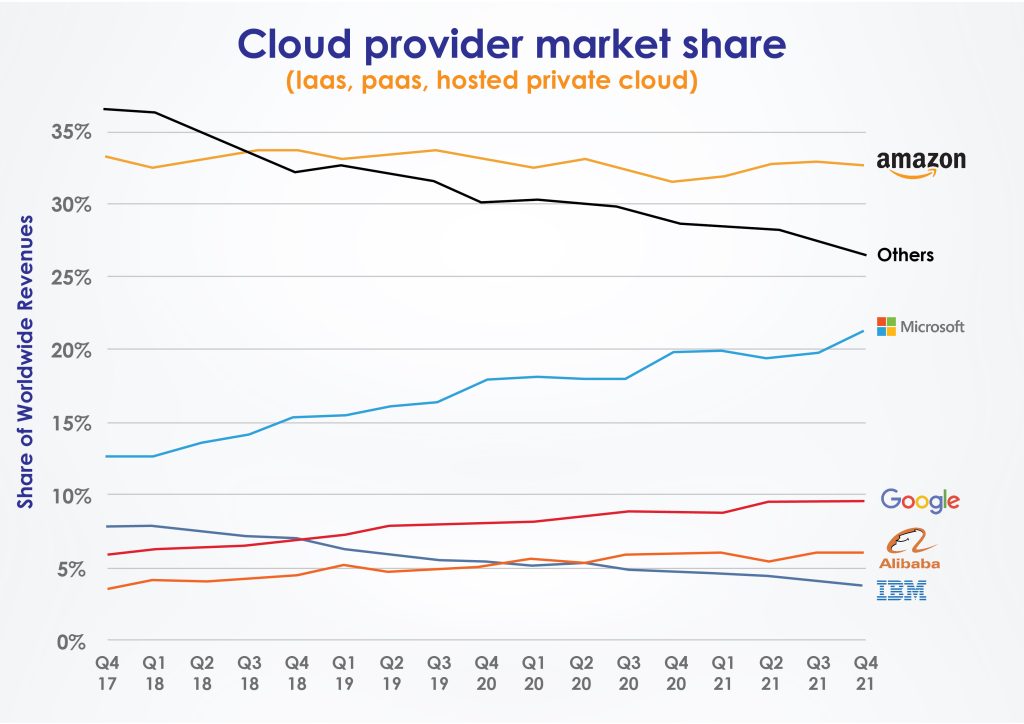
This brief guide will shine a light on the competition and services between the two market leaders in cloud services. The market is dominated by AWS (the largest single player) with a 33% market share. Microsoft Azure has only held a 21% share until Q4 2021 (up 9%). Whereas, Google Cloud Platform only holds 10% of the market.
Source: Synergy Research Group
This brief guide will shine a light on the competition and services between the two market leaders in cloud services. The market is dominated by AWS (the largest single player) with a 33% market share. Microsoft Azure has only held a 21% share until Q4 2021 (up 9%). Whereas, Google Cloud Platform only holds 10% of the market.
Azure Cloud Services
Azure Cloud Services aids in the management of applications through Microsoft-operated data centers. The platform provides seamless services like analytics, computing, networking, and storage. Its extensive toolkit is constantly growing and competing in the market with a global footprint.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS is a subsidiary of the eCommerce and technology behemoth Amazon. It has 200+ services from its globally established data centres. The pricing model and its optimized costs enable users across start-ups, large enterprises, and leading global agencies to adopt AWS.
Where the difference lies?
Gartner published a document that stated, "Public cloud services, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and IBM Cloud, are innovation juggernauts that offer highly operating-cost-competitive alternatives to traditional, on-premises hosting environments."
| AWS | Azure | |
| Data warehouse | Amazon Redshift | Azure Synapse Analytics |
| Availability | 25+ regions worldwide | 60+ regions worldwide |
| Computing | Elastic computing (EC2) | Virtual machine |
| Services | 200+ | 200+ |
| PaaS | Elastic beanstalk | App services |
| Security | AWS Identity & Access Management | Azure Active Directory |
| Serverless | AWS Lambda | Azure function |
| Containers | AWS Elastic Containers | Azure Kubernetes Services (AKS) |
| Rational database | AWS RDS | Azure SQL |
While both provide similar services, there is a certain differentiation factor as well. These can be segregated in terms of computing power, pricing, provisioning, computing, storage, features, and adaptability.
1. Computing power, provisioning, and usage
Scalability is one of the core elements of cloud computing. For Azure, users can create VMs from Virtual Hard Disks (VHD). It enables load balancing and uses virtual scale sets to ensure scalability. On the other hand, AWS uses EC2 instances in which the resource footprint may increase or shrink on demand. Users may constrict their virtual machines (VMs), which are pre-configured and users can modify them in terms of power, size, and memory.
| Service | AWS | Azure |
| Amazon Ec2 Instance | Azure Virtual machines | |
| Computing power | VMware Cloud of AWS | Azure VMware Solution |
| AWS Parallel Cluster | Azure Cycle Cloud |
In both virtual machines and servers, you can manage the OS. In both, users pay according to demand. The key differentiation is that EC2 may be customizable for various uses, whereas Azure Virtual Machines (VMs) can merge with other cloud deployment applications, even from third-party tools.
2. Storage
AWS and Azure both offer tier-based object storage. particularly directed at protecting stored data. AWS has S3 and Azure offers Azure Cool Blog Storage, both designed for infrequently accessed workloads. In terms of storage, both AWS S3-IA and Azure CBS are best for clod-tier or infrequently-accessed data loads where performance and latency are the keys.
Both offer reliable storage services ideal for long-term usage, backup, and DR. However, there are certain differences in regional availability, pricing, and security features.
3. Pricing – Comparing apples to apples
The objective of pricing comparison isn’t necessarily to make a decision between service providers but to identify where costs can be saved by using the same services from different providers. Truth be told, AWS has different pricing models, but they’re complex enough to give bill-related surprises. Dedicated tools like AWS Cost Explore, AWS Calculator, and trusted advisors are developed for cost optimization. whereas Azure’s pricing strategy is easier to understand.
Instances Selected for Comparison
(Region & Pricing Model): Middle East and Pay-as-you-go/on-demand model
Azure provides a billing dashboard with a clear bill on spending and fewer hidden charges generated from instances like AWS zombie instances. Here is an example of cloud Pricing based on-demand rates:
| Cloud provider | Instance type | vCPU | RAM (GB) |
| AWS (General purpose) | T3.Xlarge | 4 | 16 |
| AWS (Compute-optimized) | c6i.xlarge | 4 | 8 |
| Azure (General purpose) | B4ms | 4 | 16 |
| Azure (Compute Optimized) | F4sV2 | 4 | 8 |
Source: https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/pricing/on-demand/
Source: https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/pricing/details/virtual-machines/windows/
Prices are as off 3/8/2022
General Purpose
| Cloud provider | Instance type | Price |
| AWS | C6i.Xlarge | $0.3952 |
| Azure | F4sV2 | $0.4360 |
Source: https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/pricing/on-demand/
Source: https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/pricing/details/virtual-machines/windows/
Prices are as off 3/8/2022
4. Database
The next most critical decision is which database, either SQL or Non-SQL. Here is a quick comparison table-top guide for you:
| Database Service | Descriptions | AWS | Azure |
| Rational database | SQL delivers high performance, and reliability for numerous data-driven applications | RDS | SQL Database (Postgres and MySQL) |
| Non-SQL (Document storage) | Globally distributed database that supports multiple data models, key values, and documents | Dynamo DB | Cosmos DB |
| Non-SQL – Key/Value storage | Non-rational for semi-structured data | DynamoDB & Simple DB | Table Storage |
| Caching | In-memory-based service that provides- high performance, and is typically used for non-transactional work | ElastiCache | Redis Cache |
| Database migration support | Migration of database | Database Migration Service (Preview) | SQL Database Migration Wizard |
5. Analytics & Big Data processing
Now every touch point in your business generates data. These huge data volumes cannot be simply whisked away, so valuable data insights can be unearthed with the help of AWS and Azure services.
Both AWS and Azure provide the broadest selection of analytics services that are designed to enable organizations of all sizes to work with and reinvent their data. From data storage to big data analytics, streaming analytics, BI, and support for ML, both offer a broad range of services.
| Data Processing Service | Descriptions | AWS | Azure |
| Bigdata processing | Provide technologies and tools to ingest large datasets into multiple jobs | Elastic MapReduce (EMR) | HD Insights |
| Data orchestration | Move and process data within different services (usually on-prem) | Data Pipeline | Azure Data Factory |
| Cloud-based ETL data processing services that orchestrate and automate the movement of data | AWS Glue Data Catalog | Azure Data Factory + Data Catalog | |
| Analytics | Platforms that bring insights from the massive amount of data from multiple sources | Kinesis Analytics |
|
| Steaming data |
|
| |
| Data discovery |
|
| |
6. Data Warehouse
A data warehouse is a central repository for information that is extracted from multiple internal and external sources for business intelligence. The typical functionalities support data analysis, reporting, and business intelligence. The cost and technical capabilities depend on the vendors, but most data warehouses share the same traits. Compared to legacy systems, modern cloud-based data warehouse systems are agile enough to support today’s data and business intelligence requirements. Major vendors have multiple on-prem and cloud-based solutions.
Amazon and Microsoft are two of the main players in cloud computing, followed by Google and others. Amazon Redshift is a cloud-based data management system, which allows petabytes of semi-structured and structured data in little time.
Being a limitless information analysis service, Azure Synapse Analytics combines the advanced capabilities of enterprise data warehousing, data integration, and big data analytics. This allows you to query data depending on the requirements by utilizing dedicated and serverless resources.
To clarify things, here is a quick comparison between Microsoft and Amazon services in data management functionalities.
| Data Warehouse | AWS Redshift | MS Azure |
| Management and Administration | Depending upon the needs, the selection of the correct instance, size, and configuration manually | Dedicated and Serverless options are available |
| Scalability | RA3 nodes computing and decoupled storage | For the dedicated option, storage exceeding the limit will be added manually. Whereas, in serverless option scales automatically |
| Analytics Ecosystem | Its Analytics eco-system supports business intelligence with tools like AWS QuickSight | Analytics for business intelligence from PowerBI and NoSQL from CosmosDB |
| Integrations Ecosystem | Data integration with AppFlow and DMS | Azure Data Factory for data integration |
| Ingestion of Streaming Data | No built-in data support Options for ingesting streaming data:
| Yes, Apache Spark streaming functionality Alternative methods:
|
| Columnar architecture | Yes | |
| Data recovery and backup | Yes | |
| Massively Parallel Processing (MPP) | Yes | |
| Price | Depends on the cluster configuration and reserved nodes can be purchased at a discount | Can access discounted reserved storage or pricing on demand |
and
Both platforms as discussed above have strong capabilities, and it’s difficult to pick one as a clear winner. AWS has more flexibility and extra features like pricing models. Azure, on the other hand, is great when it comes to the hybrid cloud due to its great integration capabilities with Microsoft’s stack. You can make the right pick as per the requirements of the organizations. Get in touch with our cloud experts, and start your cloud journey today.
